Prostatitis is a disease characterized by the presence of inflammation and / or infection localized in the prostate gland.
May present with a wide range of clinical signs and complaints.
Anatomy
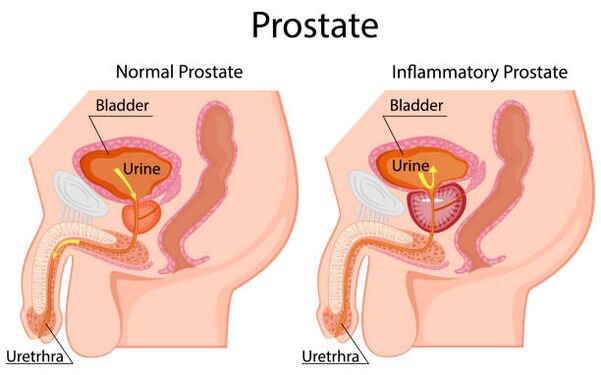
The prostate is a small gland that is part of the male reproductive system and a hormone-dependent organ. Its shape and size have been compared to a large walnut. A normal prostate gland weighs about 20 g, has a volume of 15-25 ml, and measures 3 cm in length, 4 cm in width and 2 cm in depth.
The prostate gland is located in the small pelvis, under the bladder and above the rectum. The urethra, the urethra, passes through the thickness of the gland. The prostate is surrounded by a capsule composed of smooth muscle, collagen and elastic fibers; covered with three layers of dense connective tissue (fascia) on the anterior, lateral and posterior surfaces. On the posterior surface of the prostate is bordered by the ampulla of the rectum. They are separated by the retrovesical fascia or Denonville's fascia, which allows palpation of the posterior surface of the prostate gland.
The prostate gland is approximately 70% glandular tissue and 30% fibromuscular stroma. It is customary to divide the organ into 3 zones.
Transition zone.The transition zone accounts for 10% of glandular tissue and 20% of cases of malignant prostate tumors. In this zone, one of the main age-related diseases in men is formed - benign prostatic hyperplasia, which can lead to difficulty urinating due to tissue overgrowth.
Central zone.The area surrounding the ejaculatory ducts. Consists of glandular tissue, connective tissue and muscle elements. Tumors in this area are extremely rare.
Peripheral zone.Covers the posterior and lateral sides of the prostate gland and contains 70% of the glandular tissue. This is an area that is palpable through the rectum and allows the urologist to assess the condition of the prostate gland. Up to 70% of malignant tumors are localized precisely in the peripheral zone. Therefore, digital rectal examination is an important diagnostic method and should be performed in patients over 45 years of age.
Prostate functions:
- production of prostate secretion, which is an integral part of the sperm and is involved in liquefying the ejaculate, as well as saturating it with nutrients such as various enzymes and vitamins, citric acid, zinc ions, which help to improve sperm motility and activity;
- The prostate contains smooth muscle fibers that help the release of sperm from the urethra during ejaculation, prevent sperm from entering the bladder and are involved in the mechanism of urinary retention.
Prostatitis, benign prostatic hyperplasia and prostate cancer are the three main diseases of the prostate.
All three diseases can coexist in the same prostate at the same time. That is, the presence of prostatitis does not exclude the presence of prostate hyperplasia and prostate cancer in the patient and vice versa.
Causes of prostatitis
According to statistics, prostatitis is the most common urological disease - after prostate hyperplasia and prostate cancer - in men under 50 and the third most common in men over 50.
Prostatitis accounts for 6 to 8% of outpatient urological visits.
The most common causative agent of prostatitis is E. coli strains, which are detected in 80% of cases. More rare pathogens are enterococci, Pseudomonas aeruginosa, Klebsiella and other gram-negative bacteria. The role of sexually transmitted infections (such as chlamydia trachomatis) in inflammation of the prostate is still not clearly established and is under study. In patients with HIV infection and other severe changes in the immune system, possible causative agents are cytomegalovirus, mycobacterium tuberculosis, fungi and other rare pathogens. There are data indicating the presence of microorganisms in the prostate gland that are not detected in standard studies, but play a role in the appearance of inflammatory changes and the subsequent development of symptoms of prostatitis.
Possible causes of prostatitis are:
- intraprostatic reflux of urine as a result of dysfunctional urination (urine, with certain predisposing factors, can enter the prostate gland through the prostate ducts, causing an inflammatory process);
- unprotected anal sex;
- narrowing of the foreskin (phimosis);
- autoimmune diseases;
- functional and anatomical changes in the pelvic floor muscles;
- changes in the central nervous system, including functional and anatomical changes in the brain;
- traumatic and unusual sexual activity;
- psychological factors (in a number of studies, the influence of psychological stress on the occurrence of symptoms of chronic prostatitis has been proven - in some patients psychosomatic disorders were diagnosed, in the treatment of which a decrease in prostatitis symptoms and the likelihood of its relapse were noted).
Risk factors for prostatitis also include: abstinence or excessive sexual activity, the habit of restraining ejaculation, smoking, working at night, a sedentary lifestyle, inadequate fluid intake, and poor diet.
Symptoms
- pain or burning when urinating (dysuria);
- urination disorders;
- discoloration of urine;
- the appearance of blood in the urine;
- pain in the abdomen, groin, or lower back;
- pain in the perineum;
- pain or discomfort in the penis and testicles;
- pain with ejaculation;
- increased body temperature (with acute bacterial prostatitis).
Diagnostics
According to the generally recognized classification of prostatitis NIH (US National Institutes of Health), there are four categories of disease, traditionally denoted by Roman numerals:
- I - acute bacterial prostatitis;
- II - chronic bacterial prostatitis;
- III - chronic abacterial prostatitis / chronic pelvic pain syndrome (CP / CPPS);
- IIIa - chronic prostatitis / chronic pelvic pain syndrome with signs of inflammation;
- IIIb - chronic prostatitis / chronic pelvic pain syndrome without signs of inflammation;
- IV - asymptomatic (asymptomatic) chronic prostatitis.
Despite the widespread prevalence of prostatitis, acute bacterial prostatitis is not common - 5% of all cases of the disease. But his diagnosis is quite simple, since the picture of the disease is most often pronounced: a man complains of frequent, painful urination, pain in the womb and perineum. A rise in body temperature is characteristic, and often to high values - less than 39 ° C.
Diagnosis of acute bacterial prostatitis involves a digital rectal examination (rectal examination), which involves feeling (palpating) the prostate gland with the index finger through the anus (rectum).
Digital rectal examination (DRE) is an important diagnostic manipulation if any pathology of the prostate gland is suspected. Therefore, it is advisable for men not to refuse to conduct it.
In acute bacterial prostatitis, the prostate on palpation is sharply painful, edematous, most often enlarged. Ultrasound examination can show not only an increase in the size of the prostate gland, but also foci of purulent fusion of prostate tissue (abscesses) - but this happens infrequently and, as a rule, is a consequence of a running process.
Laboratory diagnostics, first of all, includes a general urine test, in which an increase in the number of leukocytes is noted. Bacteriological urine culture is recommended. Based on the results of the analysis, it is possible to determine the presence of bacteria and their sensitivity to the antibiotic and, thus, adjust the prescribed antibiotic therapy. A general blood test is also performed to assess the general condition of the body and its response to the inflammatory process.
Taking prostate secretions for diagnosis in acute prostatitis is contraindicated due to the increased risk of a life-threatening condition: bacteremia and sepsis. Determination of the oncomarker (PSA), its fractions is also not recommended - due to the low information content and distortion of the data against the background of inflammation.
Treatment of prostatitis
Antibiotic therapy is the basic therapy for patients with prostatitis of all categories.
Alpha-blockers are also an effective group of drugs. As a result of their action, the tone of the smooth muscles of the prostate gland, the neck of the bladder and the prostatic part of the urethra decreases, thereby improving urination and reducing the possibility of urine entering the prostate gland (intraprostatic reflux of urine), which is one of the causes of prostatitis. The most effective and popular drugs are Tamsulosin and Silodosin. They are also widely used to improve urination in patients with prostatic hyperplasia.
It is possible to use anti-inflammatory drugs (Diclofenac), which effectively reduce pain and discomfort during urination, reducing prostate swelling, and also contribute to some improvement in the quality of urination.
Acute bacterial prostatitis is often a reason for hospitalization in a hospital, where antibiotic therapy in the form of intravenous injections is prescribed. After stabilization of the patient's condition, the patient continues to receive antibiotics in the form of tablets for 15 or more days in order to prevent the transition of acute prostatitis to chronic bacterial prostatitis.
According to statistics, 10% of patients with acute prostatitis develop chronic bacterial prostatitis. Another 10% of patients will develop chronic pelvic pain syndrome (chronic prostatitis IIIb) in the future.
How is the treatment of prostatitis in the clinic
Urologists treat prostatitis and other diseases of the genitourinary system, based on international clinical guidelines. This means that they use not only their professional knowledge, but also are guided by scientifically proven and accepted worldwide methods of diagnosis and therapy.
Our doctors do not prescribe ineffective drugs and examinations "just in case", do not treat non-existent diseases. When making a diagnosis, urologists rely on the data obtained from the examination of the patient, the clinical picture, the data of laboratory and instrumental studies. If surgical treatment is required, a surgical operation is performed on the territory of the clinic.